- The basic components of Japanese
- Time estimates for different proficiency levels
- Beginner level (200-400 Hours)
- Lower intermediate level (400-600 Hours)
- Intermediate level (600-1,200 Hours)
- Upper intermediate level (1,200-1,500 Hours)
- Advanced level (1,500-2,000 Hours)
- Fluent level (2,000-2,200 Hours)
Learning Japanese is an exciting yet challenging journey, and one common question learners often ask is how many hours to learn Japanese? In reality, the time it takes to master Japanese depends on various factors such as learning goals, study methods, and individual dedication. This article will help you better understand the factors that affect learning time and how to achieve your desired proficiency level in Japanese.
The basic components of Japanese
Before diving into how long it takes to learn Japanese, it’s important to understand the complexities of the language itself. How many hours do you need to learn Japanese? Japanese is fundamentally different from English in many ways, which affects the time required to learn it.
To explore why Japanese is considered a challenging language, you can read more: 10 reasons why Japan is hard to learn
The Japanese writing system
Japanese uses three distinct writing systems: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Hiragana and Katakana are syllabaries, with each character representing a syllable, while Kanji consists of Chinese characters adopted into the language.
- Hiragana and Katakana: These are relatively simple and can be learned in a few weeks of consistent study.
- Kanji: Learning kanji is more time-consuming, as there are thousands of characters, each with multiple meanings and pronunciations. Mastering around 1,000 kanji (the basic level of literacy) can take hundreds of hours.
You may want to read How to say how are you in Japanese language
Grammar and Sentence structure
Japanese grammar is quite different from English. For instance:
- The sentence structure is typically Subject-Object-Verb (SOV), meaning the verb comes at the end of the sentence.
- Particles like "は" (wa), "が" (ga), and "を" (wo) indicate the function of words in a sentence.
- Politeness levels, honorifics, and subtle differences in verb forms add complexity to communication.
These differences can make learning Japanese more challenging, but with consistent effort, learners can become familiar with these grammatical structures.
Vocabulary
Japanese vocabulary is rich and diverse, with different levels of formality and many borrowed words from English. Building a strong vocabulary is essential but can be difficult due to the multiple readings of kanji and the nuances of formal and informal speech.
Time estimates for different proficiency levels
The time it takes to learn Japanese depends on your study approach and goals. Below is a breakdown of estimated hours required to reach various proficiency levels, along with the JLPT levels that correspond to these stages.
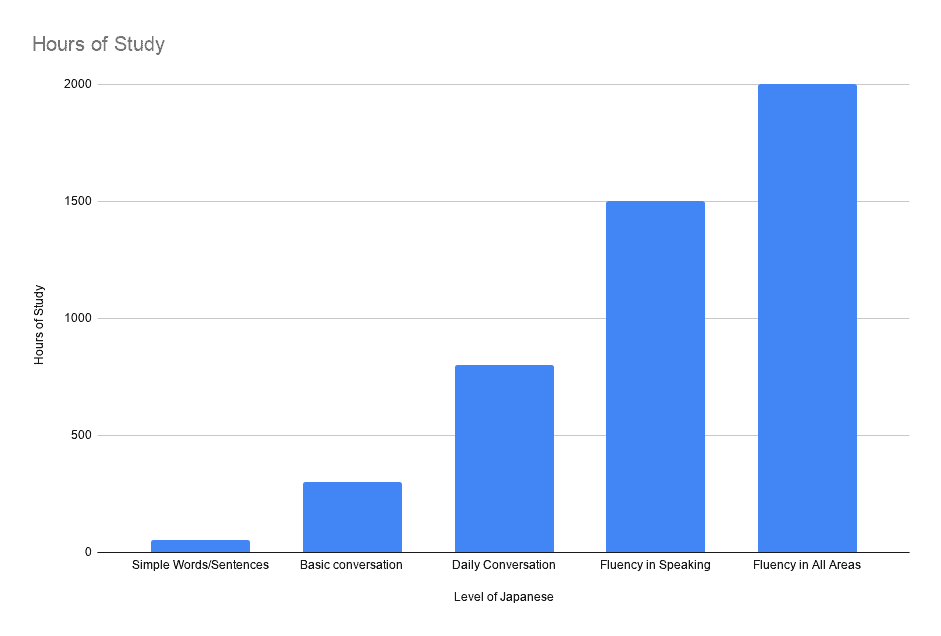
|
Proficiency level |
Estimated hours |
Focus at this level |
JLPT Level |
|
Beginner (A1) |
200-400 hours |
Mastering Hiragana, Katakana, basic vocabulary, and simple sentences. |
N5 |
|
Lower Intermediate (A2) |
400-600 hours |
Expanding vocabulary, learning basic kanji, constructing more complex sentences. |
N4 |
|
Intermediate (B1) |
600-1,200 hours |
Mastering intermediate grammar, increasing kanji knowledge (500-1,000 characters), conversational fluency. |
N3 |
|
Upper Intermediate (B2) |
1,200-1,500 hours |
Refining grammar, using more complex expressions, understanding native content. |
N2 |
|
Advanced (C1) |
1,500-2,000 hours |
Mastering advanced grammar, reading complex texts, speaking fluently with native speakers. |
N2-N1 |
|
Fluent (C2) |
2,000-2,200 hours |
Near-native proficiency, full fluency in all areas (speaking, writing, reading, and listening). |
N1 |
Read more: How to say hello in japanese
Beginner level (200-400 Hours)
At the beginner level, you’ll focus on mastering the basics of Japanese. This typically takes 200-400 hours and includes:
- Hiragana and Katakana: These syllabaries are essential for reading and writing.
- Basic Vocabulary and Phrases: Greetings, asking for directions, and ordering food.
- Simple Sentences: Constructing basic sentences like "I like sushi" or "Where is the station?"

By the end of this stage, you will be able to understand basic spoken and written Japanese. At this level, you’ll be prepared to take the JLPT N5, which is the first and most basic level of the test.
Read more: What does moshi mean in Japanese
Lower intermediate level (400-600 Hours)
The lower-intermediate level typically requires 400-600 hours of study. During this stage:
- Learning Basic Kanji: You’ll start learning around 200-300 kanji characters.
- Building Vocabulary: Expanding your vocabulary to discuss daily topics like hobbies, travel, and family.
- Intermediate Grammar: Learning more complex sentence structures and tenses.
- Conversational Practice: Being able to handle simple conversations on a variety of topics.
By the end of this level, learners can understand basic spoken Japanese and read simple materials. The JLPT N4 test corresponds to this level, which tests understanding of basic Japanese grammar, vocabulary, and kanji.
Intermediate level (600-1,200 Hours)
Achieving the intermediate level typically requires 600-1,200 hours. At this level, learners:
- Kanji mastery: Knowing around 500-1,000 kanji characters, which allows for reading more complex texts.
- Expanded vocabulary: Expanding vocabulary to talk about a variety of subjects, including more abstract concepts.
- Intermediate grammar: Mastering intermediate grammar structures like passive voice, causative forms, and more complex conjunctions.
- Fluent conversations: You can participate in conversations about a wide range of topics and can engage in basic discussions with native speakers.
The JLPT N3 corresponds to this level. It tests the ability to understand and use Japanese in everyday situations with intermediate-level vocabulary, grammar, and kanji.
Upper intermediate level (1,200-1,500 Hours)
At the upper-intermediate level, it typically takes 1,200-1,500 hours to reach fluency in reading, writing, and speaking. During this stage:
- Advanced Kanji knowledge: Learning around 1,000-1,500 kanji, allowing for more advanced reading, including news articles and books.
- Advanced grammar: Learning more subtle grammar points and expressions used in both casual and formal settings.
- Fluent communication: Being able to communicate naturally, using polite speech and understanding regional dialects.
- Native content: You can engage with TV shows, movies, and podcasts without much difficulty.

This level corresponds to the JLPT N2 test, which requires an advanced understanding of grammar, kanji, and vocabulary.
You can refer to article: How are u in Japanese
Advanced level (1,500-2,000 Hours)
The advanced level requires 1,500-2,000 hours of study. Learners at this stage:
- Complete Kanji mastery: You’ll know over 2,000 kanji characters, allowing you to read newspapers, novels, and more complex materials.
- Native-Level fluency: You’ll be able to express yourself fluently and naturally in any situation, from casual conversations to professional discussions.
- Advanced grammar proficiency: Mastery of grammar structures that distinguish native speakers, including idiomatic expressions and various levels of politeness.
The JLPT N2-N1 corresponds to this stage, with N2 being the level at which you can handle complex, nuanced conversations, and N1 being the highest level, demonstrating near-native proficiency.
You can refer to the article 11 best ways to learn Japanese vocabulary
Fluent level (2,000-2,200 Hours)
Achieving fluency in Japanese typically requires 2,000-2,200 hours of dedicated study. This level involves:
- Near-Native proficiency: Mastery of all aspects of the language, including advanced kanji (2,000+ characters), idiomatic expressions, and slang.
- Comprehensive fluency: You can read and understand any text, from academic papers to casual conversations.
- Cultural understanding: In-depth understanding of Japanese culture, regional dialects, and formal expressions.

In conclusion, the question how many hours to learn Japanese depends on your personal goals, learning methods, and dedication. While some may reach basic proficiency in a relatively short time, achieving fluency requires consistent effort and time. Remember, the journey to mastering Japanese is unique for each learner, and with the right approach, you can steadily progress toward your language goals. Stay patient and enjoy the process!








