- Japanese culture overview
- Japan culture and traditions
- Religion and Beliefs
- Customs and Rituals
- Social Values
- Japan Food Culture
- Signature dishes
- Cooking principles
- The global impact of Japanese cuisine
- Japanese family culture.
- Traditional family structure
- Role of women in the family
- Japanese Traditional Clothes
- Kimono
- Other Traditional Attire
- The influence of traditional clothing on global fashion industry
- Japanese Culture Facts
- Anime
- Manga
- Art
- Music
- Geisha
- Mount Fuji
- Patience and perfection
Discover the rich and diverse world of Japanese culture in this comprehensive guide. From traditional customs and values to iconic food and fashion, we delve into the unique aspects that define Japan. Whether you're a culture enthusiast or a first-time explorer, HeyJapan is your ultimate resource to learn and appreciate all things Japanese. Join us and experience the beauty of Japanese culture firsthand!
Japanese culture overview
Japanese culture is a blend of ancient traditions and modern influences, creating a unique and fascinating way of life. From ancient beliefs rooted in Shinto and Buddhism to contemporary pop culture phenomena like anime, Japanese culture continues to captivate the world. The harmonious blend of tradition and innovation is a hallmark of Japan, where cultural practices are deeply respected and preserved while adapting to modern times.
Japan culture and traditions
Religion and Beliefs
Religion plays a significant role in shaping Japanese culture. Shinto, Japan’s indigenous religion, emphasizes a deep reverence for nature and ancestors. Buddhism, which came to Japan from China and Korea, also has a strong influence, especially in ceremonies and spiritual practices. Together, these religions form the spiritual foundation of many traditional celebrations.
Tanabata
Tanabata, also known as the Star Festival, is a celebration based on the Chinese legend of two stars, Orihime and Hikoboshi. The festival, held on July 7th, involves writing wishes on colorful paper strips and hanging them on bamboo trees. Tanabata symbolizes hope and dreams, and is a beloved tradition in Japan.
Obon
Obon is a Buddhist custom that honors the spirits of ancestors. Celebrated in mid-August, it is a time for families to reunite and pay respects to their deceased loved ones. During Obon, it is customary to visit graves, light lanterns, and participate in Bon Odori dances to welcome spirits back home.
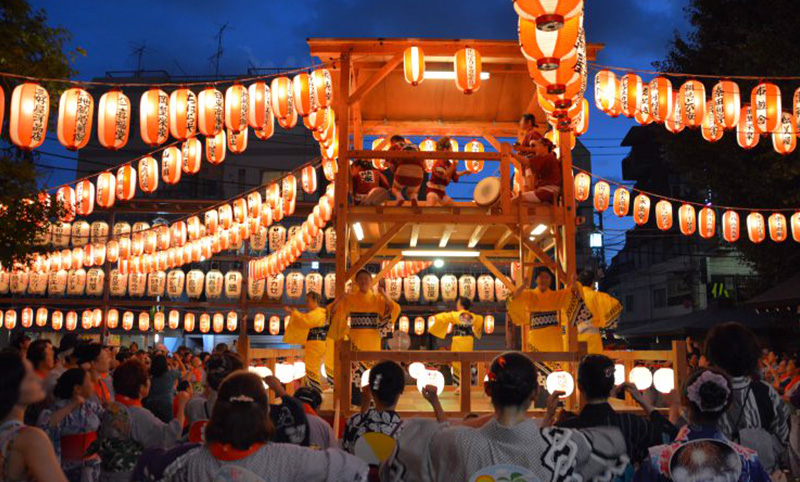

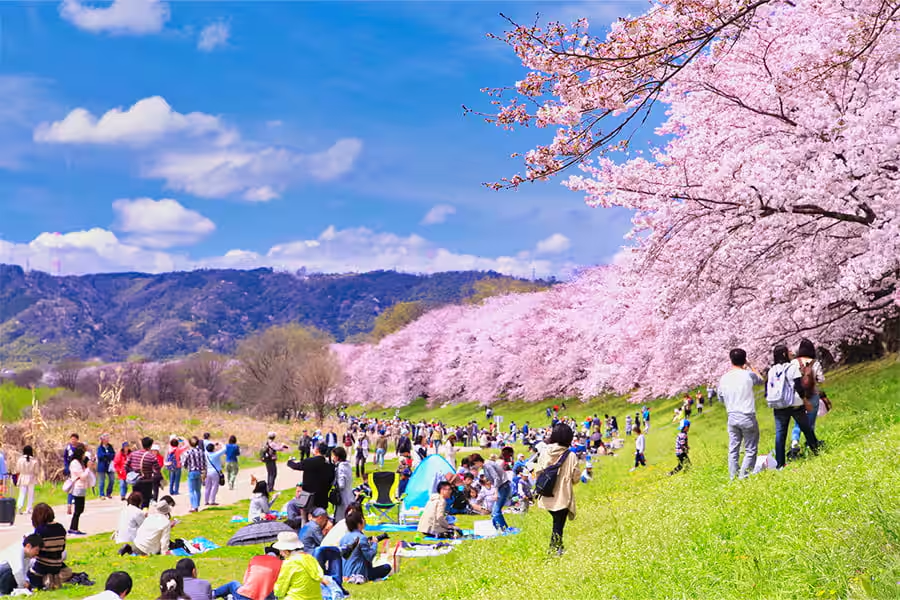
Cherry Blossom
Cherry blossoms, or "sakura," hold a special place in Japanese culture. Every spring, people gather for Hanami (flower viewing) to appreciate the beauty of cherry blossoms. This tradition symbolizes the fleeting nature of life, as the blossoms bloom for a short period before falling, reminding people to cherish the present moment.

Customs and Rituals
Japanese customs are deeply intertwined with respect and formality. Bowing, for example, is a common gesture to show gratitude, respect, and humility. Additionally, the Japanese have a ritualistic approach to many activities, including tea ceremonies, where every movement and gesture holds symbolic meaning.
Social Values
Respect, humility, and harmony are core values in Japanese society. The concept of wa, or harmony, is central to interpersonal relationships and social conduct. In the Japanese worldview, maintaining a peaceful, cooperative environment is highly valued, which is reflected in the polite and reserved nature of its people.
Japan Food Culture
Japanese cuisine is renowned for its balance of flavors, aesthetics, and emphasis on fresh ingredients. The traditional food culture is deeply influenced by the seasons, with each dish showcasing the best of what nature has to offer at any given time.
Signature dishes
Sushi
Sushi, perhaps the most famous Japanese dish, is a combination of vinegared rice and various ingredients like raw fish, vegetables, and sometimes seaweed. It is a perfect representation of Japanese cuisine’s emphasis on fresh, simple ingredients and attention to detail.
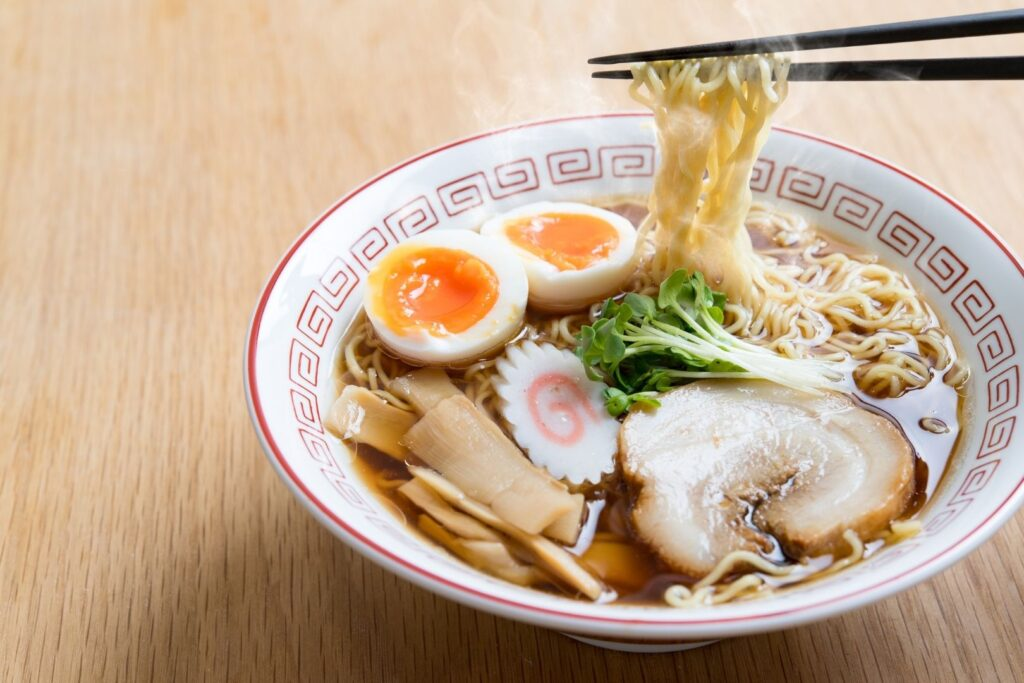
Ramen
Ramen is a popular noodle dish that originated in China but has become a staple in Japanese cuisine. It consists of Chinese-style wheat noodles served in a meat- or fish-based broth, often topped with sliced pork, nori (seaweed), and boiled eggs.

Tempura
Tempura is a method of frying vegetables or seafood in a light batter. This dish is a symbol of Japan’s ability to refine foreign influences, as it was introduced by the Portuguese in the 16th century but has become a beloved part of Japanese cuisine.
Sashimi
Sashimi is thinly sliced raw fish or seafood, often served with soy sauce, wasabi, and pickled ginger. It highlights the Japanese appreciation for fresh, high-quality ingredients and the art of presenting food in an aesthetically pleasing manner.
Okonomiyaki
Okonomiyaki is a savory pancake made with flour, eggs, cabbage, and other ingredients like pork, shrimp, or squid. This dish reflects Japan’s love for street food and casual dining, with each region offering its own variation.
Cooking principles
Japanese cooking revolves around simplicity, seasonality, and balance. The principle of "umami," often described as the fifth taste, plays a key role in Japanese cuisine. Meals are carefully prepared to create harmony between flavors, textures, and colors, ensuring that every dish complements the others.

The global impact of Japanese cuisine
Japanese food has had a significant influence worldwide, with sushi bars and ramen shops appearing in cities around the globe. The rise of Japanese culinary culture abroad reflects a growing appreciation for its healthy, diverse, and aesthetically pleasing dishes.
Japanese family culture.
Traditional family structure
The traditional Japanese family structure, known as ie, is hierarchical, with the father as the head of the family. Elders are highly respected, and children are expected to show obedience. The ie system typically involved three generations living together under one roof, but modern families have moved toward more nuclear family units. Despite changes, respect for elders and the concept of filial piety remain strong values.

Role of women in the family
Historically, Japanese women were seen as caretakers, managing the household and raising children while their husbands worked. The role of women has evolved significantly, with more women pursuing careers and contributing to family income. However, women still play a central role in family life, particularly in maintaining traditions, handling child-rearing responsibilities, and organizing family events.
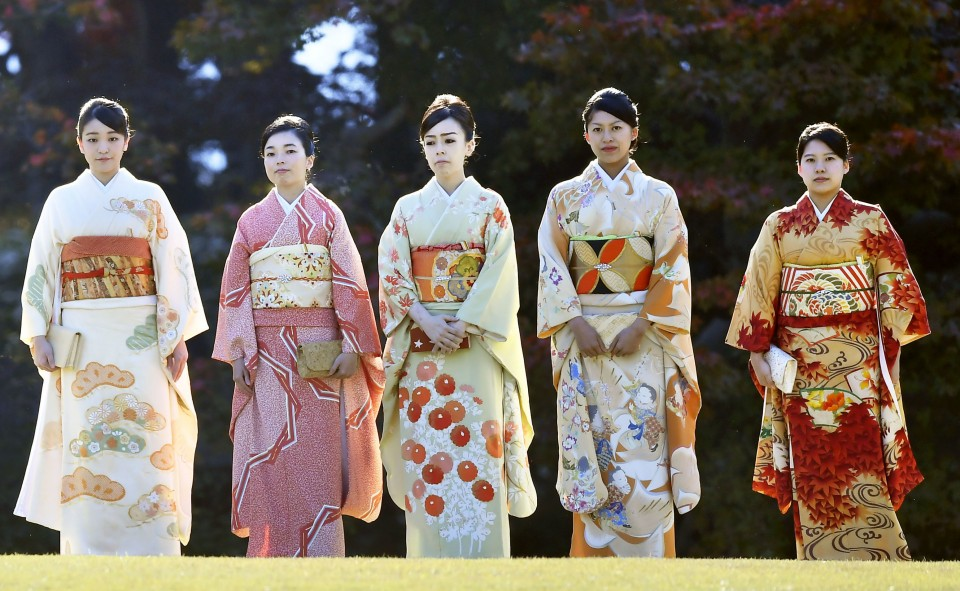

Japanese Traditional Clothes
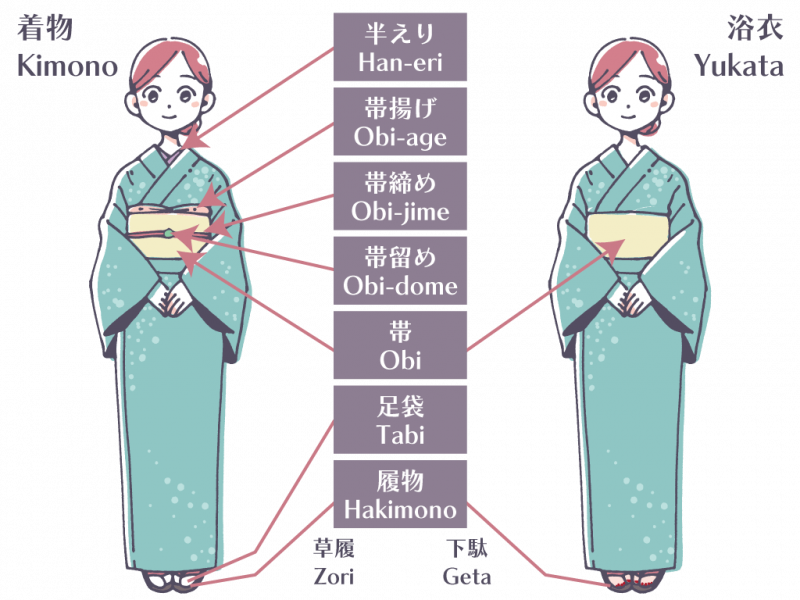
Kimono
The kimono is Japan’s most iconic traditional garment, typically made from silk and featuring intricate designs that often reflect nature, seasons, or personal status. Worn during special events such as weddings, tea ceremonies, and festivals, the kimono’s elaborate design and craftsmanship make it a symbol of Japanese culture. The garment is tied with an obi belt and is worn with specific accessories, each adding to its elegance and ceremonial importance.
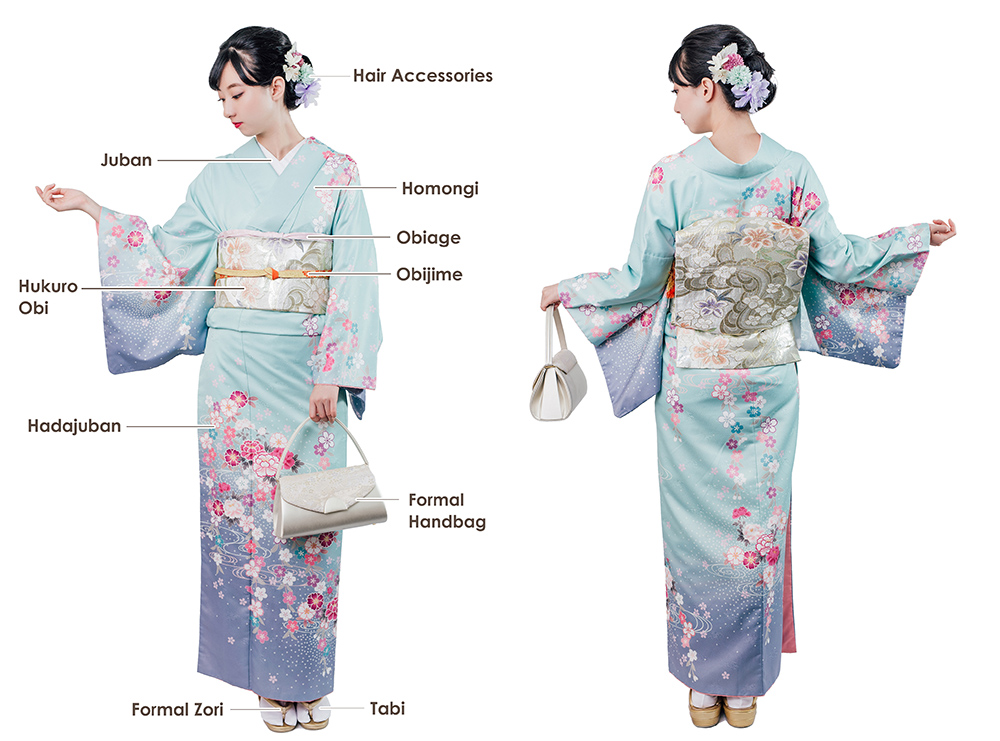

Other Traditional Attire
Aside from the kimono, Japan boasts several other traditional garments. The yukata, a casual, lighter version of the kimono, is often worn during summer festivals. The hakama, worn by both men and women for formal occasions like graduations, consists of wide pants worn over a kimono or juban (undergarment). Additionally, samurai armor and ceremonial attire for Shinto rituals, such as the montsuki kimono, showcase the cultural richness of Japan’s wardrobe.
The influence of traditional clothing on global fashion industry
Japanese traditional clothing, particularly the kimono, has had a lasting impact on global fashion. Designers like Jean-Paul Gaultier and Vivienne Westwood have incorporated kimono-inspired elements into their collections, blending Japan’s aesthetic with Western fashion trends. The minimalist beauty, unique shapes, and detailed fabric of Japanese attire have inspired everything from haute couture to streetwear, showcasing the universal appeal of Japan’s timeless craftsmanship.
Japanese Culture Facts
Anime
Japanese animation has become a global cultural phenomenon, influencing both animation styles and storytelling techniques worldwide. Popular anime series such as Naruto, One Piece, and Attack on Titan have created massive international fanbases, with many countries adapting anime's vibrant, dynamic art style and complex narratives. This genre has inspired numerous creators, reshaping the entertainment industry worldwide.

Manga
Japanese manga has had a profound influence on the global comic book industry. Manga’s unique art style and approach to storytelling have resonated with readers across different cultures. Popular titles like Dragon Ball, My Hero Academia, and Sailor Moon have been translated into multiple languages and have inspired new generations of comic book artists and writers in the West.

Art
Traditional Japanese art has left a lasting mark on Western art movements, particularly through ukiyo-e woodblock prints. Artists like Vincent van Gogh and Claude Monet drew inspiration from these Japanese prints, influencing the development of Impressionism. The minimalistic and nature-focused elements of Japanese art continue to inspire artists and designers globally.
Music
Japanese music, from traditional genres such as gagaku (court music) and taiko drumming to modern genres like J-pop and Japanese rock, has found a strong international following. J-pop artists such as Perfume and Arashi have contributed to Japan's cultural influence, and traditional Japanese instruments like the shamisen have been incorporated into global musical performances and collaborations. The unique sound and rhythm of Japanese music continue to inspire musicians across different genres around the world.
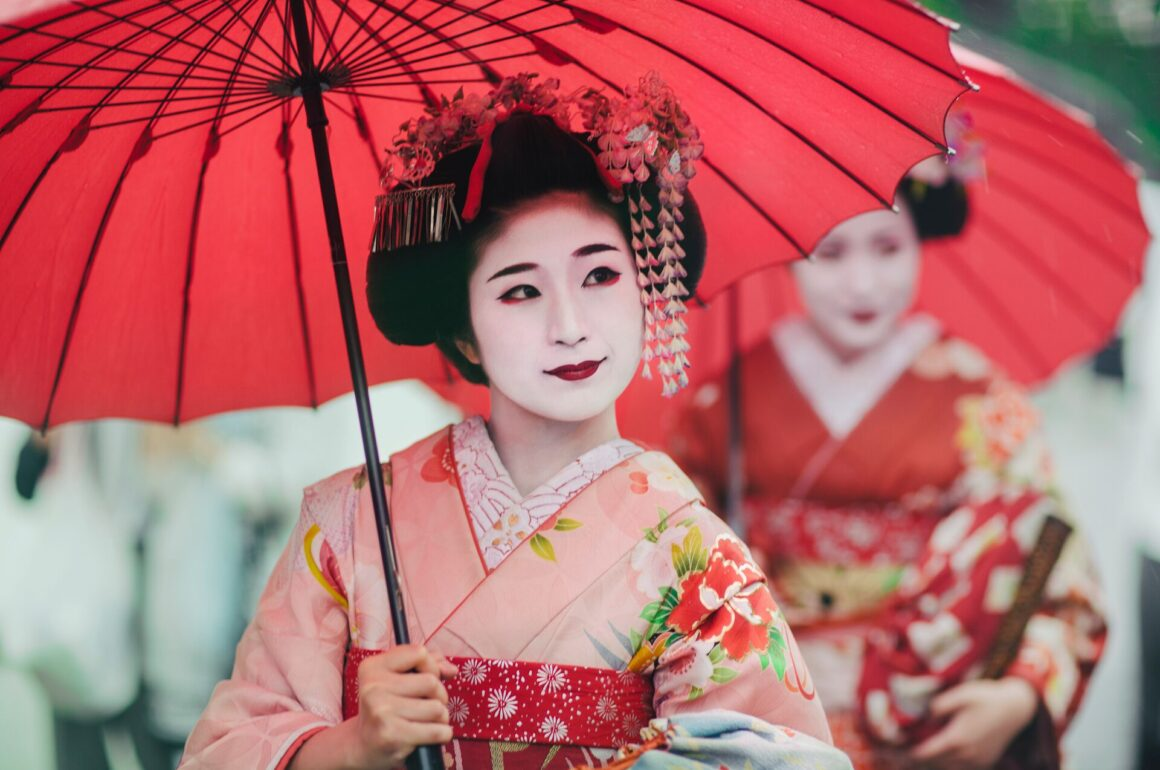
Geisha
The geisha is a symbol of Japanese elegance, grace, and tradition. These skilled women are highly trained in arts such as tea ceremonies, classical music, and dance. Geishas embody the cultural essence of Japan and are revered for their mastery of refined, timeless practices that date back centuries.

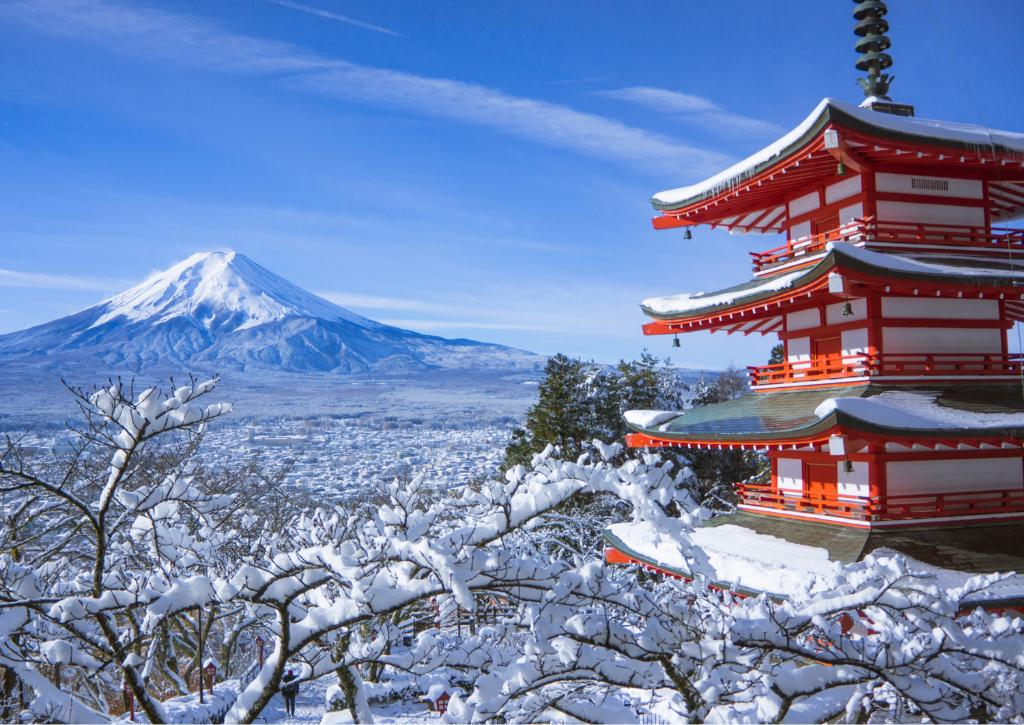
Mount Fuji
Mount Fuji, Japan’s highest peak, is not only a physical landmark but also a powerful symbol of beauty and spiritual significance. It is frequently depicted in Japanese art, literature, and poetry, representing harmony, resilience, and the natural beauty of Japan.

Patience and perfection
Patience and perfection are two foundational values in Japanese culture. The Japanese approach to craftsmanship, whether in tea ceremonies, pottery, or calligraphy, emphasizes the pursuit of perfection through meticulous attention to detail. The process of achieving perfection often takes years, reflecting the deep cultural belief that true mastery requires time, patience, and unwavering dedication to one’s craft. This pursuit of perfection is also evident in the way Japanese society values order, precision, and mindfulness in everyday life.

In conclusion, Japanese culture offers a fascinating blend of tradition, values, food, and fashion. With its rich history and unique practices, there's always something new to explore. Stay connected with HeyJapan for more insights into the incredible world of Japanese culture and deepen your appreciation of this vibrant heritage.






